Introduction
Obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass, captivates with its alluring colors that span a wide spectrum. This enigmatic gemstone has been prized for centuries, its uses ranging from ancient tools to modern-day jewelry. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of obsidian’s diverse hues.
Rainbow Spectrum of Obsidian
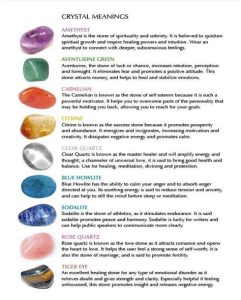
“What are the colors of obsidian?” you may wonder. Obsidian exhibits a remarkable array of colors, each with its distinct characteristics:
- Black Obsidian: The most common form, absorbing almost all light, resulting in its opaque black color.
- Brown Obsidian: Impurities, such as iron oxides, lend this type of obsidian its rich brown hue.
- Green Obsidian: Small inclusions of olivine minerals create a stunning emerald-green color, reminiscent of the tropical rainforests.
- Red Obsidian: Iron oxides impart a fiery red color to this variety, often referred to as “Apache Tears.”
- Blue Obsidian: A rare and highly prized type, its deep blue hue is caused by the presence of cobalt or copper impurities.
- Rainbow Obsidian: A combination of multiple colors, this variety displays a mesmerizing play of iridescence, resembling a rainbow trapped within the glass.
Factors Influencing Color
The specific color of obsidian is determined by several factors:
- Chemical Composition: The presence and concentration of impurities, such as iron, magnesium, and copper, influence the color.
- Crystal Structure: Obsidian’s amorphous structure allows for impurities to be trapped and distributed unevenly, creating variations in color.
- Heating and Cooling Processes: The rate of heating and cooling affects the color and clarity of obsidian.
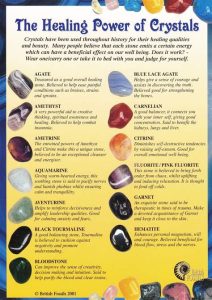
Uses and Applications of Obsidian
Obsidian has found numerous uses throughout history and present day:
- Ancient Tools: Obsidian’s sharp edges made it an ideal material for crafting tools, weapons, and arrowheads.
- Jewelry and Accessories: Its vibrant colors and smooth texture have made obsidian a popular choice for jewelry, beads, and pendants.
- Metaphysical Beliefs: Some cultures believe obsidian absorbs negative energy and promotes spiritual growth.
- Contemporary Art: Obsidian’s unique properties make it a versatile medium for contemporary artists and sculptors.
- Medical Applications: Obsidian has been used in wound dressings and surgical tools due to its antimicrobial properties.
Obsidian VS Other Gemstones
Comparing obsidian to other gemstones highlights its unique characteristics:
| Feature | Obsidian | Garnet | Jade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Range | Rainbow | Deep red | Green, white |
| Clarity | Opaque to translucent | Transparent | Translucent |
| Hardness | 5-5.5 Mohs | 6.5-7.5 Mohs | 5-6 Mohs |
| Density | 2.4-2.6 g/cm³ | 3.5-4.3 g/cm³ | 2.9-3.3 g/cm³ |
Tips and Tricks
- To enhance the iridescence of rainbow obsidian, hold it under light and move it around.
- Obsidian can be easily scratched, so handle it with care and avoid abrasive cleaners.
- Store obsidian in a dry, dark place to prevent fading.
- Clean obsidian using a soft cloth and water; avoid harsh chemicals.
Step-by-Step Guide for Carving Obsidian
- Gather necessary tools: Obsidian carving knife, water bowl, sandpaper.
- Sketch the desired design onto the obsidian surface.
- Hold the knife at a 45-degree angle and gently score the glass along the design.
- Dip the knife in water frequently to minimize friction and heat.
- Gradually increase depth and precision of cuts.
- Smooth and polish the edges using sandpaper until satisfied with the final shape.
Conclusion
Obsidian’s captivating colors and diverse applications make it a remarkable gemstone. From ancient tools to modern-day jewelry, obsidian’s versatility continues to inspire and captivate. By understanding its unique properties and embracing its beauty, we can unlock the full potential of this enigmatic volcanic glass.
Table 1: Obsidian Color Variations
| Color | Impurities |
|---|---|
| Black | Absence of impurities |
| Brown | Iron oxides |
| Green | Olivine minerals |
| Red | Iron oxides |
| Blue | Cobalt or copper impurities |
| Rainbow | Multiple impurities and iridescence |
Table 2: Comparison of Obsidian to Garnet, Jade
| Feature | Obsidian | Garnet | Jade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5-5.5 | 6.5-7.5 | 5-6 |
| Color Range | Rainbow | Deep red | Green, white |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Transparent | Translucent |
| Density | 2.4-2.6 g/cm³ | 3.5-4.3 g/cm³ | 2.9-3.3 g/cm³ |
Table 3: Tips for Enhancing Obsidian’s Iridescence
| Method | How to |
|---|---|
| Rotate Under Light | Move obsidian under bright light and rotate it to observe the play of colors. |
| Use a Magnifying Glass | Examine the obsidian’s surface with a magnifying glass to fully appreciate the iridescent patterns. |
| Backlight | Place obsidian against a light source to enhance the iridescence and create a stunning effect. |
Table 4: Obsidian Carving Guide
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Sketch Design |
| 2 | Score Glass |
| 3 | Dip Knife in Water |
| 4 | Increase Cut Depth |
| 5 | Smooth Edges |
| 6 | Polish Surface |