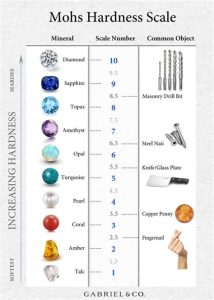
Introduction
Polished stones, also known as gemstones, have captivated humans for centuries. Valued for their beauty, durability, and rarity, these natural wonders have found myriad applications in jewelry, art, and even technology.
Polished Stones VS Other Precious Materials
- Diamonds: Harder; more brilliant; more expensive.
- Rubies: Red hue; more valuable; more brittle.
- Emeralds: Green hue; more opaque; rarer than diamonds.
- Sapphires: Blue hue; more affordable; more versatile.
Benefits of Polished Stones
Polished stones offer numerous benefits, including:
- Visual Appeal: Stunning colors, luster, and clarity.
- Durability: Resistance to scratches and wear.
- Versatility: Applications in jewelry, art, and technology.
- Investment Value: Appreciation over time.
Types of Polished Stones
The wide variety of polished stones includes:
- Diamond: The hardest known natural material.
- Ruby: A deep red variety of corundum.
- Emerald: A green variety of beryl.
- Sapphire: A blue variety of corundum.
- Topaz: A golden-yellow variety of topaz.
- Aquamarine: A blue-green variety of beryl.
Applications of Polished Stones
Polished stones have found diverse applications, such as:
- Jewelry: Rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.
- Art: Sculptures, carvings, and mosaics.
- Technology: Lasers, transistors, and optical fibers.
- Industrial: Abrasives, cutting tools, and precision instruments.
New Applications for Polished Stones
Innovative “stone-tech” applications include:
- Biomedical: Bone implants, dental fillings, and drug delivery systems.
- Energy: Photovoltaic cells and batteries.
- Electronics: Flexible displays and high-performance chips.
Strategies for Evaluating Polished Stones
To assess the quality of polished stones, consider these factors:
- Carat: Weight in carats.
- Clarity: Number and size of inclusions.
- Color: Hue, saturation, and tone.
- Cut: Shape and polish.
- Certification: Independent verification of authenticity.
How to Care for Polished Stones
Proper care ensures the longevity of polished stones:
- Clean: Use a soft cloth with mild soap and water.
- Store: Protect from sunlight, heat, and humidity.
- Inspect: Regularly check for damage or wear.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the difference between a polished stone and a gemstone?
– Polished stones are gemstones that have been processed to enhance their beauty. -
How can I identify a real polished stone?
– Seek professional certification or use a jeweler’s loupe to examine clarity and inclusions. -
What is the most expensive polished stone?
– Diamonds are generally the most expensive. -
How can I invest in polished stones?
– Purchase certified gemstones from reputable dealers.
Reviews
- “My diamond necklace has been a treasure for over two decades.” – Mary, satisfied customer
- “The emerald earrings I inherited from my grandmother are priceless.” – Sarah, heirloom lover
- “The sapphire watch I purchased is a testament to the beauty of polished stones.” – John, luxury enthusiast
- “The ruby pendant I received as a gift is truly stunning.” – Emily, admirer of beauty
Conclusion
Polished stones continue to mesmerize us with their beauty and versatility. With the rise of new technologies, the applications of these natural wonders are expanding rapidly. Whether for investment, adornment, or technological innovation, polished stones remain a timeless and valuable asset.
Tables:
Table 1: Properties of Common Polished Stones
| Stone | Hardness (Mohs) | Color | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond | 10 | Clear | Jewelry, cutting tools |
| Ruby | 9 | Red | Jewelry, lasers |
| Emerald | 7.5-8 | Green | Jewelry, lasers |
| Sapphire | 9 | Blue | Jewelry, optical fibers |
| Topaz | 8 | Golden-yellow | Jewelry, industrial |
Table 2: Comparison of Diamond Alternatives
| Stone | Hardness (Mohs) | Cost | Versatility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moissanite | 9.25 | Lower than diamond | Limited |
| Zirconia | 8.5 | Lower than diamond | High |
| Sapphire | 9 | Lower than diamond | High |
| White Topaz | 8 | Much lower than diamond | High |
Table 3: Effective Strategies for Evaluating Polished Stones
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Carat | Weight in carats |
| Clarity | Inclusions and blemishes |
| Color | Hue, saturation, tone |
| Cut | Shape and polish |
| Certification | Independent verification |
Table 4: Step-by-Step Approach to Caring for Polished Stones
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Clean with soft cloth and mild soap |
| 2 | Rinse thoroughly with water |
| 3 | Dry with soft cloth |
| 4 | Store in protective container |
| 5 | Inspect regularly |