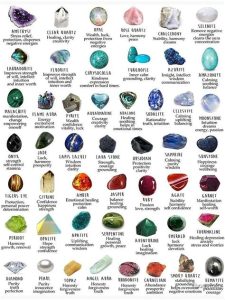
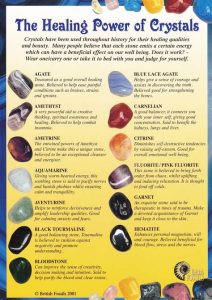
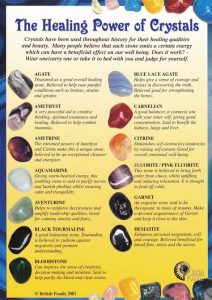
Shining Bright: Silver Stones vs. Metallic Stones
Silver stones, with their shimmering surfaces and lustrous hues, have captivated people for centuries. Metallic stones, on the other hand, possess a more muted and earthy charm. But which of these remarkable materials reigns supreme?

Hardness and Durability
Silver, with a Mohs hardness of 2.5-3, is significantly softer than metallic stones, which typically range from 5-7. This difference in hardness makes metallic stones more resistant to scratching and abrasion, rendering them ideal for jewelry and construction.
Luster and Reflectivity
Silver stones exhibit a brilliant luster, reflecting light with unmatched brilliance. Metallic stones, in comparison, have a more subdued luster, reflecting only a fraction of the light that strikes their surface.
Density and Weight
Silver stones are considerably denser than metallic stones, with a density of approximately 10.5 grams per cubic centimeter compared to around 7-8 grams per cubic centimeter for metallic stones. This difference in density makes silver stones heavier and more substantial.
Cost and Availability
Silver is a relatively rare metal, resulting in its higher cost compared to metallic stones, which are more abundant. Silver stones, therefore, tend to be more expensive and exclusive.
Silver Stones vs. Ceramic Stones: Unearthing Distinctions
The allure of silver stones extends beyond their beauty to their versatility. Ceramic stones, crafted from fired clay, offer a compelling alternative with unique characteristics.
Thermal Conductivity and Insulation
Silver stones possess excellent thermal conductivity, rapidly transferring heat throughout their structure. Ceramic stones, conversely, are poor conductors of heat, making them ideal for use in thermal insulation applications.
Electrical Conductivity and Resistance
Silver is an exceptional electrical conductor, with a high conductivity value. Ceramic stones, on the other hand, are generally non-conductive, offering high resistance to electrical currents.
Brittleness and Fracture Strength
Silver stones are inherently brittle, susceptible to breakage under stress. Ceramic stones exhibit greater fracture strength, making them more resistant to cracking and shattering.
Applications and Uses
Jewelry and Accessories: Silver stones adorn exquisite jewelry, watches, and accessories, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication. Ceramic stones, with their vibrant colors and durability, are frequently employed in jewelry and fashion accessories.
Construction and Architecture: Metallic stones find widespread application in construction and architecture, from cladding and roofing to flooring and countertops. Silver stones, with their rarity and cost, are used sparingly in these applications, often for decorative or accent purposes.
Industrial and Engineering: Silver’s electrical conductivity makes it invaluable in electrical components and contacts. Ceramic stones, due to their high-temperature resistance and wear resistance, are employed in industrial settings, including furnaces, heat exchangers, and cutting tools.
Medical and Healthcare: Silver’s antibacterial and antimicrobial properties make it useful in medical applications, such as wound dressings and surgical instruments. Ceramic stones, with their biocompatibility and inert nature, are used in dental and orthopedic procedures.
The Promise of Silver Stones: Unlocking New Applications
The allure of silver stones extends beyond their traditional uses. By harnessing their unique properties, we unlock a realm of innovative and groundbreaking applications.
Catalysis and Energy Storage: Silver’s catalytic activity makes it promising for use in fuel cells, batteries, and other energy storage devices.
Nanotechnology and Medicine: Silver nanoparticles exhibit exceptional antibacterial and antiviral properties, offering potential applications in drug delivery, wound healing, and disease diagnostics.
Sensing and Imaging: Silver’s electrical conductivity and optical properties make it suitable for sensors, detectors, and imaging systems.
Electronics and Communications: Silver’s high electrical conductivity and low resistance make it ideal for use in advanced electronic devices and high-speed communication networks.
The Silver Lining: A Cost-Benefit Perspective
The acquisition of silver stones comes with both advantages and disadvantages, warranting a careful assessment of their cost and benefits.
Benefits:
- Unparalleled luster and brilliance
- Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity
- Antibacterial and antimicrobial properties
- Versatility in applications
Costs:
- Relatively high cost compared to metallic and ceramic stones
- Softness and susceptibility to scratching
- Limited availability and potential supply constraints
The Bottom Line: Silver Stones vs. the Alternatives
The choice between silver stones and their alternatives depends on the specific application and desired properties. For applications requiring exceptional luster, conductivity, or antibacterial properties, silver stones remain the preferred choice. Metallic stones offer superior hardness and durability, while ceramic stones provide excellent thermal insulation and fracture strength. Ultimately, the decision rests on a careful consideration of the unique characteristics of each material and their alignment with the project’s requirements.
Conclusion
Silver stones, with their captivating beauty and versatile properties, continue to inspire awe and innovation. As we delve deeper into their potential, we unlock a world of groundbreaking applications, harnessing the power of these lustrous treasures.