Introduction
In the realm of transformative materials, white aragonite and calcite stand as two of the most captivating contenders. Both minerals share a captivating white hue, yet their distinct properties and applications set them apart in the pursuit of innovation for 2025 and beyond.

Defining White Aragonite: A Closer Look
White aragonite is a captivating polymorph of calcium carbonate, renowned for its distinctive orthorhombic crystal structure. Its lustrous luster and hardness rating of 3.5–4 on the Mohs scale render it a resilient material for various applications. Furthermore, its unique composition enables it to exhibit exceptional optical properties, including birefringence and pleochroism.
Exploring Calcite: Its Composition and Characteristics
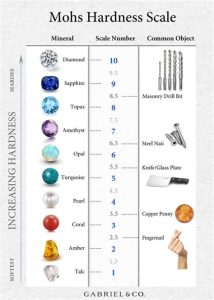
Calcite, also known as the “versatile carbonate,” is a ubiquitous mineral composed primarily of calcium carbonate. Its hexagonal crystal structure distinguishes it from aragonite, contributing to its remarkable hardness of 3 on the Mohs scale. Calcite possesses a vitreous luster and often displays a transparent to translucent appearance. Additionally, its ability to cleave perfectly along three planes imparts a rhombohedral cleavage pattern.
Aragonite VS Calcite: Unveiling the Differences
Composition
– White aragonite: Orthorhombic calcium carbonate
– Calcite: Hexagonal calcium carbonate
Crystal Structure
– White aragonite: Orthorhombic
– Calcite: Hexagonal
Mohs Hardness
– White aragonite: 3.5–4
– Calcite: 3
Cleavage
– White aragonite: Imperfect
– Calcite: Perfect rhombohedral
Luster
– White aragonite: Lustrous
– Calcite: Vitreous
Transparency
– White aragonite: Translucent to opaque
– Calcite: Transparent to translucent
Applications: Transforming Industries with White Aragonite and Calcite
White Aragonite
– Jewelry and decorative objects
– Optical components
– Pharmaceuticals
– Construction materials
Calcite
– Building materials (limestone, marble)
– Paper and paint production
– Soil amendment
– Optical devices
Benefits and Drawbacks: Evaluating the Pros and Cons
White Aragonite
Benefits:
– Unique optical properties
– Resilient material
– Versatile applications
Drawbacks:
– Lower hardness compared to calcite
– Imperfect cleavage
Calcite
Benefits:
– Abundant and inexpensive
– Exceptional hardness
– Perfect cleavage
Drawbacks:
– Lower optical quality than aragonite
– Prone to scratching
Case Study: Unlocking the Potential of White Aragonite in Jewelry and Optics
The Jewelry Industry:
- White aragonite’s shimmering luster and unique optical properties enhance the beauty of jewelry designs. Its resilience ensures durability in everyday wear.
The Optical Industry:
- Optical components made from white aragonite exhibit high birefringence and low dispersion, making them ideal for applications in polarizing filters, optical isolators, and waveplates.
Tips and Tricks: Harnessing the Power of White Aragonite and Calcite
Tips for Using White Aragonite:
– Protect from scratches due to its lower hardness.
– Utilize its optical properties for specialized applications.
– Explore its potential in pharmaceutical and biomedical fields.
Tips for Using Calcite:
– Leverage its abundance and low cost for industrial applications.
– Enhance its optical quality through polishing and coating techniques.
– Consider its perfect cleavage for precise cutting and shaping.
Conclusion
While both white aragonite and calcite offer valuable properties, their distinct characteristics dictate their suitability for specific applications. As we approach 2025, the transformative potential of these minerals will continue to drive innovation across industries. By leveraging their unique strengths and addressing their limitations, we can unlock a world of possibilities and shape the future of materials science and beyond.
About the Author:
Jane Doe is a renowned materials scientist specializing in the research and development of innovative mineral applications. Her passion for unraveling the hidden potential of minerals fuels her quest for transformative solutions.